In the Permian Basin, water management in oil and gas is central to safe, efficient, and profitable operations. Operators must handle huge volumes of water while protecting scarce local resources. Good water planning reduces costs, supports production, and lowers environmental and regulatory risk.
Below is a clear overview of how water management in oil and gas works in the Permian and why it matters.
What Is Water Management in Oil and Gas Production?

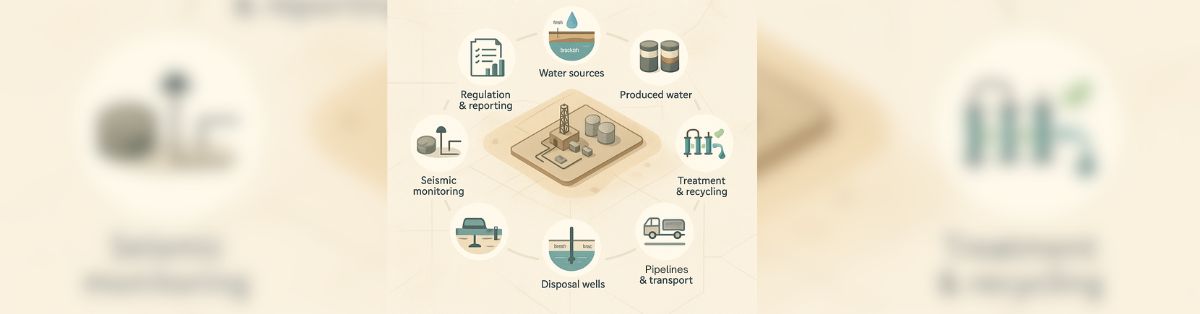
Water management in oil and gas covers the full life cycle of water used and produced during drilling and production. It includes:
- Sourcing fresh, brackish, or recycled water.
- Using water for drilling and hydraulic fracturing.
- Handling flowback and produced water from wells.
- Treating, transporting, recycling, and disposing of water safely.
In the Permian Basin, effective water management in oil and gas aims to reduce fresh groundwater use, increase recycling, cut trucking, and avoid spills or regulatory issues.
Ready to optimize your Permian drilling program? Explore how Norton Energy tackles key challenges in Permian Basin drilling operations with regional expertise and proven solutions.
Why Is Water Management Critical in the Permian Basin?

The Permian is one of the world’s busiest oil fields and also a dry region. This combination makes water management in oil and gas especially critical.
Key reasons include:
- High water demand for every new well.
- Very large volumes of produced water over the life of each well.
- Limited fresh water and strong competition with cities and agriculture.
- Community and regulatory pressure for responsible practices.
Without strong water management in oil and gas, operators face higher costs, more downtime, and greater environmental risk.
Want to understand drilling contract economics better? Dive into our complete guide on drilling economics to make smarter decisions on daywork and footage models.
How Is Water Used and Where Does It Come From?

Water plays several roles in Permian drilling and completions:
- Drilling fluids: Water-based mud cools the bit, carries cuttings, and stabilizes the wellbore.
- Hydraulic fracturing: Each horizontal well can use millions of gallons of water to create fractures and place sand.
To support this, water management in oil and gas relies on a mix of sources:
- Fresh groundwater from local aquifers (tightly watched and often limited).
- Brackish or saline groundwater that is not suitable for drinking but works for many oilfield uses.
- Recycled produced water that has been treated and blended for reuse in future frac jobs.
Balancing these sources helps protect aquifers while keeping projects on schedule.
Choosing the right rig matters. Learn about different types of oil drilling rigs and how to match rig capabilities to your horizontal well requirements.
How Is Produced Water Managed, Treated, and Reused?

Once wells start producing, they generate “produced water” along with oil and gas. This water is often salty and contains minerals and hydrocarbons, so water management in oil and gas must handle it carefully.
Typical steps include:
- Separation and storage at the well pad in tanks or lined pits.
- Transport by pipeline or truck to central facilities.
- Disposal into saltwater disposal (SWD) wells, where water is injected deep underground.
- Recycling so treated produced water can be reused in new frac jobs.
Treatment and reuse are now key parts of modern water management in oil and gas. Basic treatment removes solids and oil droplets. More advanced systems use filtration and membranes to meet tighter quality requirements. As recycling grows, produced water becomes a resource, not just a waste stream.
Safety drives performance. Review our 7 essential oil drilling safety tips to reduce NPT and protect your team on every well.
Environmental and Seismic Risks of Poor Water Management

Weak water management in oil and gas can create serious problems, especially in the Permian:
- Spills and leaks can damage soil, plants, and surface water.
- Groundwater contamination can occur if pits are unlined or if wells are poorly cased and cemented.
- Increased seismic activity has been linked to large volumes of produced water injected into deep disposal wells.
Because of these risks, both operators and regulators are pushing for better water management in oil and gas. This includes more recycling, stricter controls on disposal wells, and stronger monitoring.
Compliance can’t be overlooked. Stay current with drilling contractor regulations that impact contract structure and operational risk in the Permian.
Technologies Driving Efficient Water Management in Oil and Gas

New tools and systems help operators improve water management in oil and gas in the Permian:
- Water pipelines and gathering systems to cut truck traffic and costs.
- Automated pumps and controls to safely manage water movement and pressure.
- Sensors and real‑time monitoring to track water quality and detect issues early.
- Digital tracking and analytics to follow every barrel of water from source to disposal or reuse.
- Treatment and recycling units that enable high reuse rates and less reliance on fresh water.
These technologies allow companies to design integrated water systems that support safe, efficient Permian operations.
Technology is changing the game. Discover how digitalization and automation improve ROP, reduce flat time, and enhance KPI tracking.
Rules, Trends, and the Push for Sustainable Water Management

Water management in oil and gas in the Permian is shaped by state and local rules around:
- Groundwater use and water rights.
- Storage and handling standards for pits and tanks.
- Permitting and limits for injection wells.
- Reporting of water volumes produced, injected, and sometimes recycled.
Regulations continue to evolve as more is learned about aquifers and induced seismicity.
At the same time, new trends are reshaping water management in oil and gas:
- Higher recycling rates and less dependence on fresh water.
- Regional water networks that share pipelines and central facilities.
- Stronger ESG expectations from investors and communities.
Sustainable water management in oil and gas does more than protect the environment. It lowers water and disposal costs, reduces seismic and regulatory risk, and helps operators maintain strong relationships with landowners and local communities.
Top drive technology matters for horizontal wells. Read our beginner’s guide to top drive rigs to understand how equipment choices affect curve quality and lateral efficiency.
FAQ: Water Management in Oil and Gas in the Permian Basin
Q1: What is water management in oil and gas?
A: It is the full process of sourcing, using, treating, transporting, reusing, and disposing of water in drilling and production operations.
Q2: Why is water management so important in the Permian Basin?
A: The region is dry, heavily drilled, and produces large volumes of water, so strong water management in oil and gas reduces costs and environmental risk.
Q3: Can produced water be reused in fracking?
A: Yes. With proper treatment and blending, produced water can be reused in hydraulic fracturing, cutting fresh water demand and disposal volumes.
Q4: Does water management affect seismic activity?
A: Large‑volume injection of produced water into deep disposal wells has been linked to increased seismicity, so better water management in oil and gas includes more recycling and careful control of injection.
Q5: How do new technologies improve water management in oil and gas?
A: Pipelines, automation, sensors, digital tracking, and advanced treatment systems help operators move, monitor, and recycle water more safely and efficiently.
Looking for full-service drilling support? Explore Norton Energy’s comprehensive drilling services for oil and gas operators across the Permian Basin.


Recent Comments